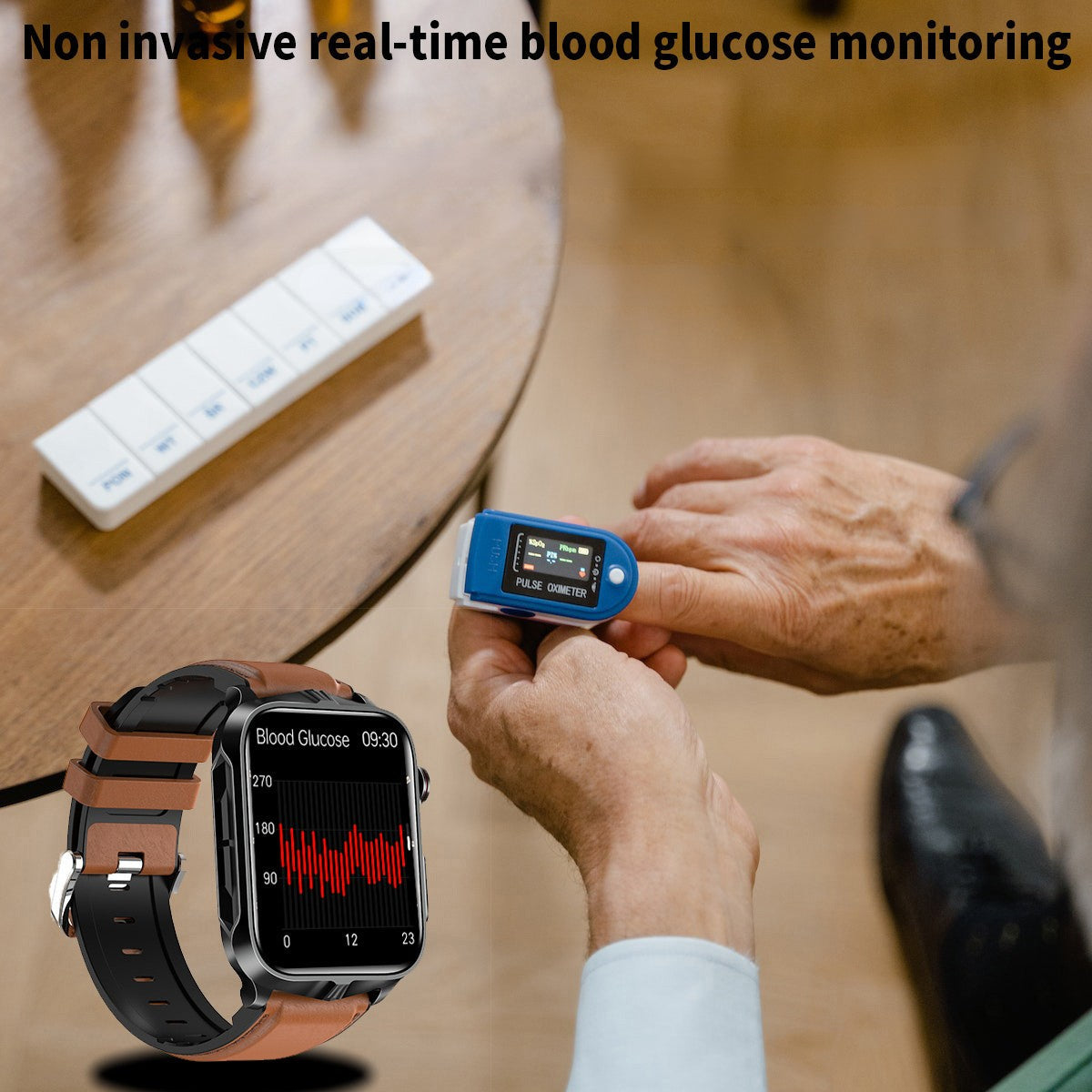
Imagine checking your blood sugar as casually as you check the time. No needles, no test strips—just a flick of your wrist. This vision is inching closer to reality as tech giants and startups race to integrate non-invasive glucose monitoring into smartwatches. For the 38 million Americans with diabetes and millions more at risk, this innovation could be life-changing. Here’s how your future smartwatch might keep your blood sugar in check—and why it’s not just sci-fi anymore.
Why Smartwatches? The Promise of Pain-Free Tracking
For decades, glucose monitoring meant finger pricks or wearing a sensor with a tiny needle (CGM). While CGMs like Dexcom and Freestyle Libre have revolutionized diabetes care, they’re still invasive, costly, and require regular replacements. Smartwatches, already worn daily by 1 in 5 Americans, offer a seamless alternative:
- 24/7 monitoring: Track trends while sleeping, eating, or exercising.
- Discreet and stigma-free: No visible patches or devices.
- Holistic health insights: Pair glucose data with heart rate, activity, and sleep metrics.
The goal? A device that quietly guards your metabolic health, alerting you to spikes or crashes before they escalate.
How It Works: The Tech Behind the Magic
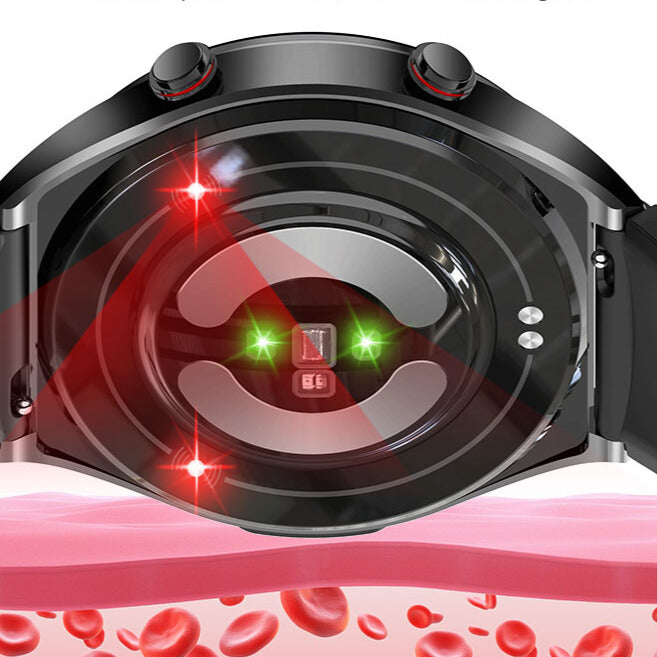
Non-invasive glucose tracking in smartwatches relies on cutting-edge methods to “read” blood sugar through the skin. Here’s what’s in development:
1.Optical Sensors (Light-Based Tech)
How it works: Shine near-infrared (NIR) or laser light into the skin. Glucose molecules absorb specific wavelengths, and sensors analyze the reflected light to estimate blood sugar levels.
2. Radiofrequency (RF) and Spectroscopy
How it works: Emit low-power electromagnetic waves through the skin. Glucose levels alter the wave’s properties, which are measured to calculate concentrations.
3. Multi-Sensor Fusion
How it works: Combine optical, thermal, and bioimpedance sensors to cross-validate data and improve accuracy.
Example: A smartwatch might use PPG (heart rate), SpO2 (blood oxygen), and sweat analysis to infer glucose trends.
While no smartwatch today offers FDA-approved glucose monitoring, the race is heating up.
In 2023, a UCSD team published a study showing smartwatch-compatible optical sensors achieved 85% accuracy compared to blood tests—a promising leap.
Real-World Impact: Who Wins?
Diabetics: Eliminate finger pricks and CGMs’ $300+/month cost.
Prediabetics: Catch insulin resistance early with real-time feedback on diet and exercise.
Fitness Buffs: Optimize workouts by tracking how carbs fuel (or crash) their energy.
Case Study: A Reddit user testing a prototype smartwatch noted, “After pizza, my watch buzzed: ‘Glucose rising fast.’ I took a walk, and the spike flattened. Mind-blowing.”
The Future: What’s Next for Smartwatch Glucose Tech
Hybrid Systems: Watches that pair non-invasive sensors with weekly fingerstick calibrations for higher accuracy.
AI-Driven Alerts: Predictive algorithms that warn, “Blood sugar may drop in 30 minutes—eat a snack.”
Integration with Ecosystems: Sync glucose data with insulin pumps (like Tandem’s) for automated diabetes management.
Beyond Diabetes: Track metabolic health for weight loss, athletic performance, or longevity.
How to Prepare for the Glucose-Smartwatch Era
Stay Informed: Follow updates from Apple, Samsung, and startups like PoalarHealth.
Protect Your Data: Ensure any experimental device complies with HIPAA and data privacy laws.
Manage Expectations: Early versions may be “wellness tools,” not medical devices—check with your doctor before relying on them.
Non-invasive glucose monitoring in smartwatches isn’t a matter of if but when. While technical and regulatory hurdles remain, the potential to transform diabetes care—and empower millions to take control of their health—is undeniable. Until then, keep your eye on that sleek device on your wrist. Soon, it might do more than count your steps; it could save your life.
Join the POALARHEALTH,Find Your Fit: https://www.poalarhealth.com/